Referral
An 8-year-old male neutered border collie was referred to the oncology team to discuss radiotherapy options for a left sided cavernous sinus meningioma.
Patient History
The patient initially presented to his family veterinarian for evaluation of two grand mal seizures while out for a walk on 15/11/2017. The seizure activity continued in hospital, and he was referred to a local referral hospital and he was referred to a local referral hospital for further work up.
Diagnostics
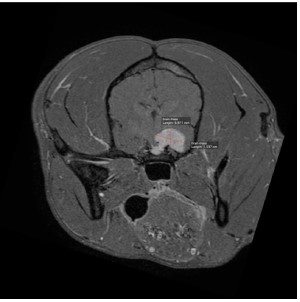
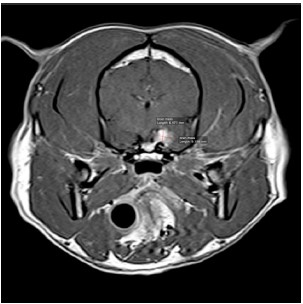
An MRI was done, and images detected a broad based extra axial contrast enhancing mass in the left cavernous sinus region consistent with a meningioma. The mass was deemed non resectable, and phenobarbital and prednisolone were initiated. He was referred to the oncology team on 30/11/2017 to discuss radiotherapy options. CT simulation for radiation planning was done on 4/12/2017 and stereotactic radiotherapy was initiated on 6/12/2017.
Outcome
The patient did well throughout the course of therapy with no observable acute affects. However, seizure activity continued and Keppra was started on 8.1/2018. Intermittent seizure continued after this change and phenobarbital was substituted with zonisamide on 22/1/2018. The combination of Keppra and zonisamide was effective in controlling seizure activity. A follow up MRI was done on 8/6/2018 and documented a 60% decrease in tumour volume. The patient presented in July 2021 with recurrent symptoms and proceeded to a second course of radiotherapy and passed away 15 months later 5 years after initial diagnosis.
Stereotactic radiation therapy (SRT) 3 day course of treatment to thelleft cavernous sinus mass.

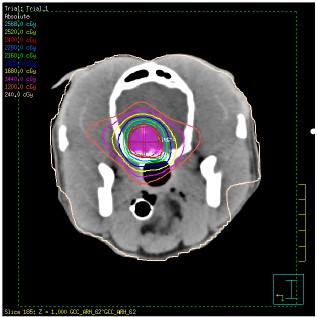
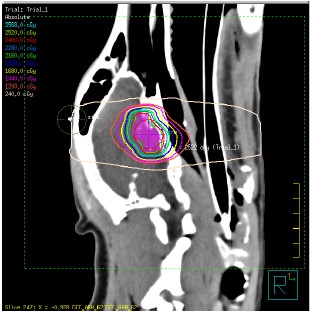
SRT was prescribed to the cavernous sinus meningioma as a non-surgical alternative. Treatment was delivered via volumetric arc therapy (VMAT)

24Gy in 3# to the left nasal mass

VMAT fields are used to provide excellent treatment, preserving healthy tissue and critical surrounding structures

Treatment was planned via CT planning scan.

15 minute treatment time with daily image guided radiation therapy (IGRT) used to verify the accuracy and precision of treatment.